Procedure of Handling Appeals, Complaints and Dusputes
ENG
KOR
ENG
KORA system in which large-scale GHG emitting businesses are allocated emission allowances and fulfill their reduction obligations directly and through market mechanisms.

Organizations designated as participants in emission trading schemes are required to report their greenhouse gas emissions to the government based on emission calculation plans derived from emission allocation schemes. Korean Foundation for Quality (KFQ) offers highly reliable greenhouse gas emission statement verification services.
A system that establishes goals for GHG reduction, energy saving, and energy use efficiency in large-scale businesses on the basis of the Framework Act on Low Carbon, Green Growth and the Enforcement Decree of the Act through consultation between the management company and the government, and manages the implementation through incentives and penalty systems.
Target management firms are required to report their greenhouse gas emission statement to the government after undergoing verification by external verification agencies. Korean Foundation for Quality (KFQ) provides highly reliable verification services for target management emission statements.

Management company designation
(Y)

Submission of specifications
(Y+1-)

Setting reduction targets
(Y+1-)

Establishment of implementation plan
(Y+1-)

Obejective achievement
(Y+2-)

Report on compliance with
sepecification submission(Y+2-)
The Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) is one of the flexibility mechanisms defined in the Kyoto Protocol(IPCC, 2007) that provides for emissions reduction projects which generate Certified Emission Reduction units which may be traded in emissions trading schemes. The CDM addresses the second objective by allowing the Annex I countries to meet part of their emission reduction commitments under the Kyoto Protocol by buying Certified Emission Reduction unites from CDM emission reduction projects in developing countries.

KFQ, as Designated Operational Entity (DOE),is responsible for CDM-related validation and verification/certification activities as well as for VCS/GS
| 1 | Energy industries (renewable/non-renewable Sources) |
|---|---|
| 2 | Energy distribution |
| 3 | Energy demand |
| 4 | Manufacturing industries |
| 5 | Chemical industry |
| 9 | Metal production |
| 11 | Fugitive emissions from production and consumption of halocarbons and sulphur hexafluoride |
| 13 | Waste handing and disposal |
| 15 | Agriculture |
The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) is a system implemented by the European Union (EU) to impose carbon costs on non-EU companies producing products imported into the EU at a level equivalent to the carbon costs imposed on EU-based companies subject to the EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS). This mechanism aims to prevent carbon leakage, where European companies relocate their manufacturing facilities to non-EU countries with relatively lower carbon costs due to the high carbon costs within the EU, and to achieve the climate goals of the EU.
Initially targeting industries such as steel, aluminum, cement, fertilizers, hydrogen, and electricity, CBAM is expected to expand to a more diverse range of products in the future, considering the risk of carbon leakage.
 Monitoring |
 Reporting |
 Monitoring |
 Reporting |
 Verification |
 Purchase and Submission of CBAM Certification |
CBAM is scheduled to be fully implemented from 2026 after a transitional period from October 2023 to December 2025. During the transitional period, importers bringing targeted products into Europe must report greenhouse gas emissions information received from manufacturers at the time of customs clearance. Subsequently, during the definitive period, importers must report verified emissions, obtained through qualified verification bodies, and purchase and pay for CBAM certificates corresponding to the carbon costs. Although verification is not mandatory during the transitional period, the EU recommends the company may voluntarily have emissions data verified by an independent verifier accredited to ISO 14065, or according to the rules of the eligible MRV system.
Korean Quality Foundation has been approved by the Korean Standards Institute as a validation/verification body in accordance with KS Q ISO/IEC 17029 and ISO 14065. It has established high recognition and trust in various greenhouse gas verification markets, including domestic emission trading schemes. Additionally, it participates in government agencies' response committees for CBAM adaptation, swiftly grasping relevant trends and contributing to informing domestic companies.
Article6 of the Paris Agreement is an international mechanism to promote greenhouse gas reduction through international cooperation, replacing the existing CDM with a new international carbon market system.
Article 6.4 of the Paris Agreement is an international mitigation project mechanism operated by the UNFCCC under the supervision of the CMA (Conference of the Parties to the Paris Agreement). KFQ is currently undergoing the process to be accreditated as a Designated Operational Entity (DOE) for validation/verification of Article 6.4 projects.

(Sources : https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/article-64-mechanism)
Upcoming uploads after the accreditation process is complete
Upcoming uploads after the accreditation process is complete
attached
·Person in charge : Seok-won Lee, Team Leader of Verification management Team
·Email : ghg_vt@kfq.or.kr
·Telephone number : 02-6277-9432
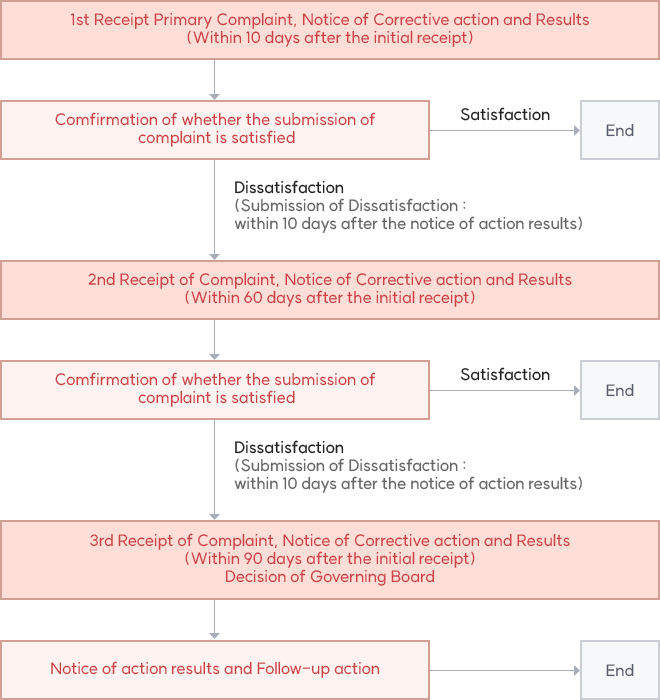

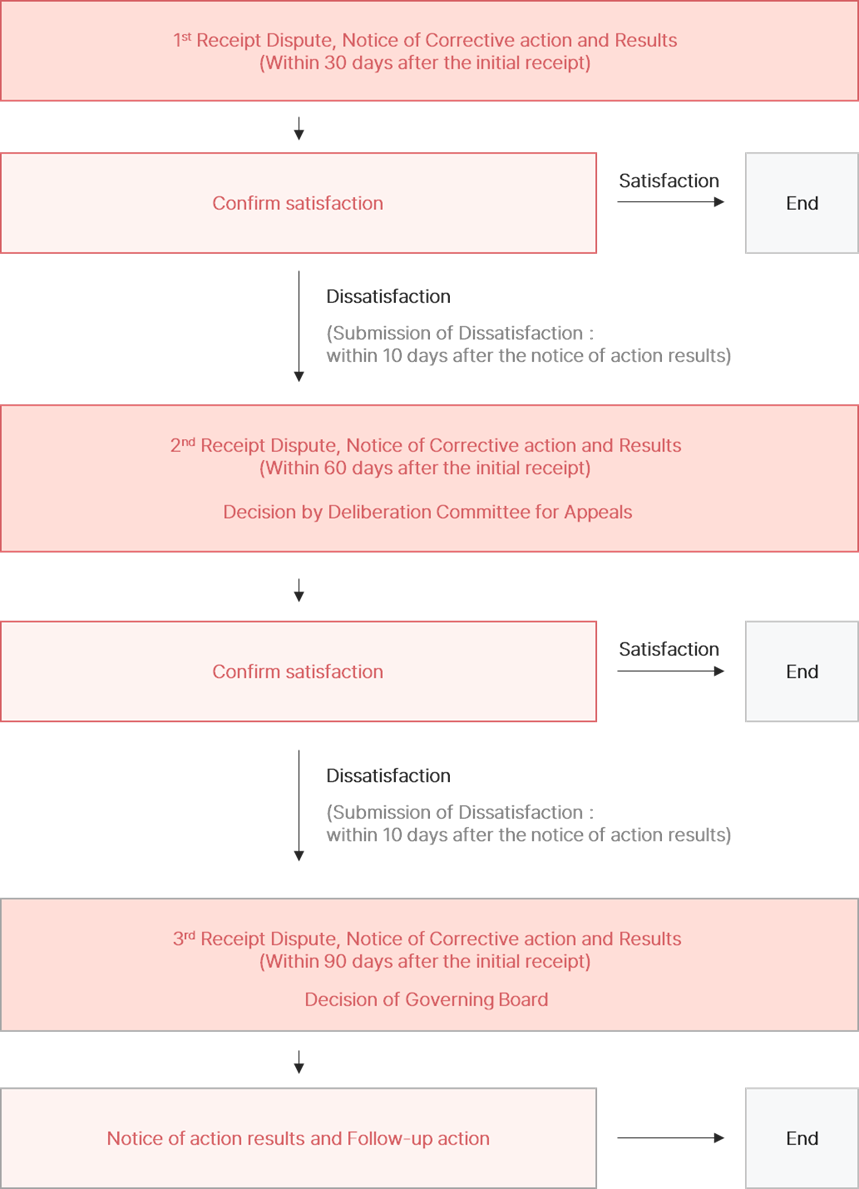
Procedure of Handling Appeals, Complaints and Dusputes
It is indirect GHG emissions from the organization's value chain. While not directly regulated, such as Scope1 emissions directly into the atmosphere within organizational boundaries and Scope 2 emissions from external power and heat consumption, there is a growing interest in Scope 3 emissions as the demand for sustainability increases.

Source : Technical guidance for calculating scope 3 emissions, WRI & WBCSD
Verification of Scope 3 emissions offers various benefits. While Scope 1 and 2 are mostly subject to regulations, Scope 3 presents opportunities for additional greenhouse gas reduction beyond organizational boundaries as there are no reduction obligations. By verifying Scope 3 emissions, organizations can identify energy efficiency and cost-saving opportunities in their value chains, collaborate with suppliers to implement sustainable initiatives, and thereby reduce greenhouse gas emissions from their products. Korean Foundation for Quality (KFQ), as South Korea's first private-sector greenhouse gas verification agency, leverages extensive and diverse verification experience across all industrial sectors to provide specialized Scope 3 verification services based on required standards.
It is a unit used to report the results of Life Cycle Assessment* of the environmental aspect of a product in which a producer calculates the footprint of a specific product in accordance with international standards, etc.
* Life Cycle Assessment: Estimating and Evaluating the potential environmental impact of inputs and outputs throughout Life Cycle (from Raw material extraction to Disposal of products)
Results of Life Cycle Assessment of a specific product are verified by a third party in accordance with international standards and information is delivered to stakeholders through a verification opinion. The system can be recognized externally by overseas stakeholders by applying international standards such as PAS2050, ISO/TS 14067, GHG Protocol, ISO 14044. Korean Foundation for Quality(KFQ) provides reliable and professional verification services with approval from the Operating institution according to KS Q ISO/IEC 17029, ISO 14065.
The Gold Standard (GS), established in 2003 by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and international NGOs, is an organization and standard designed to address the shortcomings of the Kyoto Mechanisms' Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) in reflecting contributions to sustainable development and enhancing social, economic, and environmental benefits of carbon projects.
In the voluntary carbon market, as opposed to the regulated carbon market, emission reduction credits are issued and traded based on greenhouse gas (GHG) reductions achieved by privately-led projects. The Gold Standard certifies the GHG reduction achievements according to its standards, ensuring both the reduction of GHGs and the project's sustainability, while also preventing greenwashing. Gold Standard conducts rigorous monitoring to uphold these standards. Representative projects include renewable energy, cookstove distribution, nature conservation, afforestation/reforestation, agriculture and soil improvement, and water purification system distribution.
The Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) is a non-profit organization that originated in the United Kingdom in 2000. It is a global climate change response initiative operating in approximately 91 countries. As of 2023, more than 23,000 companies worldwide, including 875 companies in Korea, disclose their carbon emissions, climate change risks and opportunities, and climate change response goals and strategies through CDP.
CDP evaluates companies in three main areas: Climate Change, Water Security, and Forests. The results of these evaluations are used as credible ESG assessment factors, providing essential information for investment decisions and corporate value assessments by financial institutions globally.
Starting in 2024, CDP has aligned its questionnaire with the IFRS S2 climate-related disclosure standards. Additionally, CDP’s standards are being harmonized with other reporting frameworks, including the EU’s ESRS, the U.S. SEC’s climate disclosure guidelines, and the TNFD (Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures). CDP is also enhancing its integration with climate-related initiatives such as SBTi, RE100, and NZAM, thereby strengthening its connectivity with various ESG disclosure systems.
In South Korea, the Korea Sustainability Investing Forum (Kosif) serves as the CDP partner (CDP Korea Committee). To enhance the reliability of information within CDP, an independent third-party verification system for CDP corporate reports has been implemented since 2017.The Korea Quality Assurance (KQA) has been designated by the CDP Korea Committee as the verification body. KQA verifies the CDP Response reports prepared by companies, ensuring that they are appropriately compiled according to guidelines and reviewing the credibility of both qualitative and quantitative data included in the reports.
01
 Document Review
Document Review
02
 On-site Verification
On-site Verification
03
 Verification Audit
Verification Audit
04
 Internal Review
Internal Review
05
 Issuance of Verification Statement
Issuance of Verification Statement